|
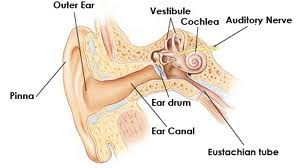
There are many disorders of the middle ear.
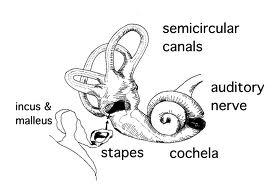
Disorders Of The Middle EarA conductive hearing loss involves the breakdown or obstruction of some part of the external or middle ear which transmits or conducts the physical vibrations of sound through air, bone or tissue. Otitis MediaIs the presence of fluid in the middle ear. Suppurative Otitis MediaIs an infection of the middle ear usually caused by bacteria from a cold or other respiratory infection. Germs enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube becomes blocked, trapping fluids in the middle ear cavity. The disease may be acute, (severe, but of short duration) or chronic (recurring or lasting a long time) In the acute stage pus collects in the middle ear cavity and causes hearing loss. The pressure of pus causes pain. The eardrum appears bright red instead of its normal colour pinkish-gray. Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaWhen infection occurs repeatedly, the perforation in the pars tensa portion of the eardrum will not heal. Infection erodes some parts of the ossicular chain; scar tissue also causes hearing loss, further impeding the action of the ossicular chain. This loss is usually permanent, with the passage of time the perforation becomes larger. Aero Otitis MediaOr Barotrauma occurs when the Eustachian tube does not open properly, for example after an airplane flight or while skin diving. Serious fluid collects in the middle ear. The drum appears normal, but with a bluish or yellowish light reflex. Often, a fluid line or bubbles appear behind the drum.
Mucoid Otitis MediaOr middle ear effusion or “glue ear” . A cold, allergy, or respiratory infection blocks the Eustachian tube and traps fluid in the middle ear. Antibiotic treatment destroys the bacteria, but the fluid remains trapped because of the plugged Eustachuian tube. Treatment is usually a myringotomy, or inflation of the Eustachian tube. If left untreated, this fluid can change the tissues of the musous membrane lining, form scar tissue, and cause further hearing loss. OtosclerosisIs a disease which causes spongy changes in the bony capsules surrounding the inner ear. This causes a hearing loss of 60-65 db often accompanied by tinnitus. Otosclerosis occurs more often in women than in men and more often in Caucasians than in other races. The disease is inherited, so otosclerosis “may run in families”. Pregnancy often triggers the onset of otosclerosis. Ossicular DiscontinuityCan occur in the presence of a loud sound, slap to the head, accidents etc. The bones in the ossicular chain no longer fit together properly, altering the leverage capabilities of the middle ear. Ossicular FixationCan occur when ossification involves the ligaments of the ossicular chain. When this involves the eardrum, it is tympanosclerosis. This often occurs in people with osteoarthritis.
In Stapes MobilizationThe stapes footplate is directly manipulated, to free it from the new growth, and allow normal movement. A successful manipulation of the stapes eliminates the conductive component of the hearing loss. In StapedectomyA tiny plastic or steel strut replaces the completely replaces the removed stapes. In FenestrationThe eardrum and most of the ossicles were removed and a tiny window (a fenestra) about the size of a grain of rice, was made through the bony wall into the horizontal semi-circular canal. CholesteatomaIs a tumor occurring in the attic of the middle ear. It sometimes perforates the pars flaccid area of the eardrum and invades the external auditory canal. TinnitusOr ringing in the ears is often present in conductive losses, usually a low frequency sound. Teeth Missing, Ill Fitting DenturesCongenital ProblemsPresent at birth can also create conductive loss. Cleft palate, or problems at birth are examples.
|