|
Outer Ear Disorders
Outer Ear DisordersMalformations of the ear, include atresia (closure) of the external auditory canal and malformed or missing auricle, “ cauliflower ear”. These malformations may cause hearing loss. Impacted cerumenImpacted Cerumen(wax)is a common cause of a conductive hearing loss. Sometimes cerumen accumulates in the canal, forming a plug, which partly or completely blocks the canal.The plug is a brown, yellow, or reddish mass if it is wet, or a black mass if it is dry (common in the older population). If the outer ear blockage is partial, there is little or no hearing loss. If the blockage is complete, or impacted, hearing loss always occurs. *Although difficult to think of wax as a disorder, this is probably the moat common disorder for this part of the ear. *Can lead to a hearing loss, however 99% blockage may not cause a loss. *The hearing loss would rarely account for more than a 30dB conductive loss. *Build up of wax is something affecting the natural migration. In older people the migration process slows down. When people work in noisy or dirty work environments wax production may be increased. Excessive use of cotton buds may push the wax further into the ear. *The best course of action is removal by a hearing health care professional. * The biggest problem to hearing aid users is feedback (whistling) and blockage of the sound outlet can cause the aid to suddenly stop working. Visit my store for a great range of Earwax removal products at LOW PRICES!
Eczema or DermatitisMakes the external ear itchy and painful. The skin of the external auditory canal becomes red and swollen. This condition will not cause a hearing loss unless the swelling blocks the canal. Otitis Externa is an inflammation of the walls of the external auditory canal. Polyps,Are masses of tissue that grow outward from a surface. Prolapsed CanalAssociated with the ageing process, is a breakdown or sag of tissue around the canal. It causes the wall of the canal to collapse.
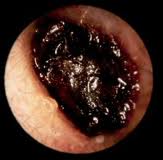
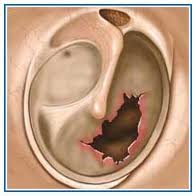
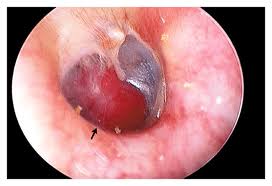
PerforationsOr ruptures are holes in the eardrum. They are caused by infection, a foreign object, a bone fracture, a nearby explosion, or a blow on the ear with the palm of the hand. Small holes often heal in a few weeks. Larger perforations require a surgical technique, tympanoplasty or myringoplasty to “patch” the hole.
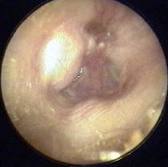
Fluid DrainageCan be odious or clear. Monomeric SpotsThese look like a hole, but they reflect light from an otoscope , like a mirror. These spots are holes that have healed and are only one layer thick. They are called mirror membranes as well.
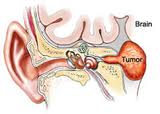
Tumor or Cholesteatoma,Another outer disorder, occurring in the middle ear, sometimes perforates the upper portion of the eardrum, invading the external auditory canal. There is a constant odorous discharge from the outer ear.
Canal Stenosis (narrowing)Narrowing of the external canal may develop as a result of trauma to the skin. The skin becomes inflamed and this is what causes the narrowing.The trauma may be caused by external laceration, chronic self-manipulation or chronic otitis externa. There are usually no symptoms unless there is an accumulation of wax and debris causing conductive hearing loss.In some cases the canal may be reduced to a tiny pinhole behind which keratin may be trapped. In some cases surgery may be required.Stenosis,Can also be found as a consequence of otitis externa. Inflammation from the infection has also caused a narrowing of the ear canal.StenosisCan also happen where the cartilage of the ear canal has broken down and this causes the canal to collapse or even close. This commonly happens as we get older and is due to deterioration of the cartilage fibre due to ageing.
|